风萧萧_Frank
以文会友加速!全球去美元化
去美元化如火如荼!东盟讨论减少金融交易对美元依赖,转向使用本币结算
华尔街见闻
周二东盟各国财长和央行行长正式会议开幕,首要议题是讨论如何减少金融交易对美元、欧元、日元和英镑的依赖,转向以当地货币结算。东盟10国也开始商讨放弃美元结算了。
据“东盟简报”网站29日报道,3月28日周二,东盟各国财长和央行行长正式会议在印度尼西亚开幕。会议的首要议题是讨论如何减少金融交易对美元、欧元、日元和英镑的依赖,转向以当地货币结算。
根据报告,会议讨论了通过本币交易(LCT)计划减少对主要货币依赖的努力。这是之前已经开始在东盟成员国之间实施的本币结算(LCS)计划的延伸。
这意味着东盟跨境数字支付系统将进一步扩大,并允许东盟国家使用当地货币进行贸易。印度尼西亚、马来西亚、新加坡、菲律宾和泰国于2022年11月就此类合作达成了协议。
他认为,印尼需要保护自己不受地缘政治动荡的影响,理由是美国、欧盟及其盟友因俄乌冲突而对俄罗斯金融业实施制裁。
佐科说,为了保护交易不受“可能的地缘政治影响”,有必要远离西方支付系统。
在东盟国家中,只有新加坡对俄罗斯实施了制裁,而所有其他东盟国家继续与俄罗斯进行贸易。人们对陷入美国主导的二级制裁感到担忧,这些制裁对涉及棉花制造业的中亚和南亚国家都有影响,而棉花制造业是该地区就业数百万人的主要行业。
值得注意的是,包括巴西等南美洲国家也在寻求替代美元的方案。
3月29日周三,巴西政府表示,已与中国达成协议,未来两国可直接使用本币进行贸易,而不必使用美元作为中间货币。
ASEAN Finance Ministers and Central Banks Consider Dropping US Dollar, Euro and Yen, Indonesia Calls for Phasing Out Visa and Mastercard
https://www.aseanbriefing.com/news/asean-finance-ministers-and-central-banks-consider-
An official meeting of all ASEAN Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors kicked off on Tuesday (March 28) in Indonesia. Top of the agenda are discussions to reduce dependence on the US Dollar, Euro, Yen, and British Pound from financial transactions and move to settlements in local currencies.
The meeting discussed efforts to reduce dependence on major currencies through the Local Currency Transaction (LCT) scheme. This is an extension of the previous Local Currency Settlement (LCS) scheme that has already begun to be implemented between ASEAN members.
This means that an ASEAN cross-border digital payment system would be expanded further and allow ASEAN states to use local currencies for trade. An agreement on such cooperation was reached between Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines, and Thailand in November 2022. This follows from Indonesia’s banking regulator, stating on March 27 that the Bank of Indonesia is preparing to introduce its own domestic payment system.
Indonesian President Joko Widodo has urged regional administrations to start using credit cards issued by local banks and gradually stop using foreign payment systems. He argued that Indonesia needed to shield itself from geopolitical disruptions, citing the sanctions targeting Russia’s financial sector from the US, EU, and their allies over the conflict in Ukraine.
Moving away from Western payment systems is necessary to protect transactions from “possible geopolitical repercussions,” Widodo said.
Of the ASEAN nations, just Singapore has enforced sanctions on Russia, while all other ASEAN nations continue to trade with the country. There has been alarm at being caught up in US-led secondary sanctions, as are short to impact Central and South Asia countries involved in cotton manufacturing, a major industry in the region employing millions of people.
Foreign investors in Asia may wish to consider the amount of US dollars, Euros and Yen held in their accounts in light of a pending ASEAN currency trade decision. Professional discussions should be taken regarding any movement of company funds to alternative currencies.
https://twitter.com/WallStreetSilv/status/1639674952658845701?ref_src=
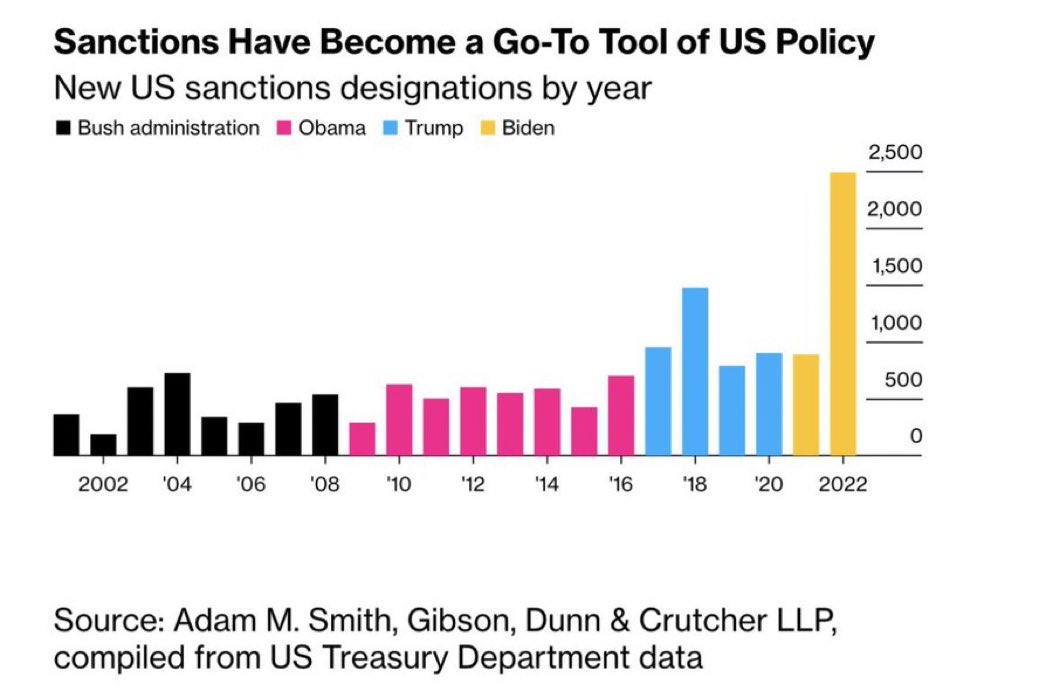
There is a reason other countries are trying to do trade settlement in their local currencies. The US is accelerating de-dollarization by issuing 10,000 unilateral sanctions on foreign entities over the last two decades! And under Biden it is accelerating.
中俄 本币结算 Sino-Russian trade is settled in local currency.
东盟去美元化 Association of Southeast Asian Nations decides to de-dollarize
巴西 与中国本币结算 Trade between Brazil and China is settled in local currency
非洲泛非支付结算系统 Pan-African Payment and Settlement System, cross-border payments in African currencies, simplifying cross-border trade.
沙特 人民币结算 Saudi Arabia and China are settled in RMB.
印尼总统佐科 减少西方支付体系 Indonesian President Joko Widodo wants to reduce the use of Western payment systems
Backfire: The Global Ripple Effects of U.S. Sanctions
February 28, 2023 1:00 PM—2:00 PM EST
Sanctions have become the go-to foreign policy tool for the United States. Coercive economic measures such as trade tariffs, financial penalties, and export controls affect large numbers of companies and states across the globe. But while U.S. policymakers see sanctions as a low-cost tactic, these measures also have potent side effects that, in some cases, can even harm American interests.
In her new book Backfire, Agathe Demarais explores the surprising ways sanctions affect multinational companies, governments, and ultimately millions of people around the world. Drawing on interviews with experts, policymakers, and people in sanctioned countries, she examines the unintended consequences of the use of sanctions as a diplomatic weapon.
Backfire: How Sanctions Reshape the World Against U.S. Interests
https://www.amazon.com/Backfire-Sanctions-Reshape-Against-Interests/dp/0231199902?
Center on Global Energy Policy Series
Nov 15, 2022
by Agathe Demarais (Author)
Sanctions have become the go-to foreign policy tool for the United States. Coercive economic measures such as trade tariffs, financial penalties, and export controls affect large numbers of companies and states across the globe. Some of these penalties target nonstate actors, such as Colombian drug cartels and Islamist terror groups; others apply to entire countries, including North Korea, Iran, and Russia. U.S. policy makers see sanctions as a low-cost tactic, but in reality these measures often fail to achieve their intended goals―and their potent side effects can even harm American interests.
Backfire explores the surprising ways sanctions affect multinational companies, governments, and ultimately millions of people around the world. Drawing on interviews with experts, policy makers, and people in sanctioned countries, Agathe Demarais examines the unintended consequences of the use of sanctions as a diplomatic weapon. The proliferation of sanctions spurs efforts to evade them, as states and firms seek ways to circumvent U.S. penalties. This is only part of the story. Sanctions also reshape relations between countries, pushing governments that are at odds with the U.S. closer to each other―or, increasingly, to Russia and China.
Full of counterintuitive insights spanning a wide range of topics, from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine to Iran’s COVID response and China’s cryptocurrency ambitions, Backfire reveals how sanctions are transforming geopolitics and the global economy―as well as diminishing U.S. influence. This insider’s account is an eye-opening, accessible, and timely book that sheds light on the future of sanctions in an increasingly multipolar world.
制裁已成为美国的首选外交政策工具。 贸易关税、经济处罚和出口管制等强制性经济措施影响着全球大量公司和国家。 其中一些处罚针对的是非国家行为者,例如哥伦比亚贩毒集团和伊斯兰恐怖组织; 其他适用于整个国家,包括朝鲜、伊朗和俄罗斯。 美国政策制定者将制裁视为一种低成本策略,但实际上这些措施往往达不到预期目的——其强大的副作用甚至会损害美国的利益。
《适得其反》探讨了制裁对跨国公司、政府以及最终影响全球数百万人的令人惊讶的方式。 通过对专家、政策制定者和受制裁国家人民的采访,Agathe Demarais 审视了将制裁用作外交武器的意外后果。 随着各州和公司想方设法规避美国的处罚,制裁的扩散刺激了逃避制裁的努力。 这只是故事的一部分。 制裁还重塑了国家之间的关系,促使与美国不和的政府彼此更加亲近——或者越来越多地与俄罗斯和中国亲近。
从俄罗斯入侵乌克兰到伊朗的 COVID 反应和中国的加密货币野心,Backfire 充满了涵盖广泛主题的违反直觉的见解,揭示了制裁如何改变地缘政治和全球经济——以及削弱美国的影响力。 这位内部人士的叙述是一本令人大开眼界、通俗易懂且及时的书,阐明了在日益多极化的世界中制裁的未来。
加速!短短48小时全球发生一个重大变化
发布:2023年03月30日 16:03来源:中时新闻网
过去48小时内,世界上多国同时发生重大货币与贸易政策转变,首先开启第一枪的是中国大陆与法国石油公司完成首笔以人民币进行贸易结算的液化天然气(LNG),紧接著沙乌地国王批准了该国加入上合组织(SCO)也包含其中的贸易联盟,再来则是中国大陆和巴西敲定了以2国货币进行贸易结算的协议,最后则是东协10国(ASEAN)财长和央行开始展开放弃美元、欧元和日元的会议,并且呼吁淡化VISA, Mastercard等外国支付系统。
综合外媒报道,本周二(28)中国海洋石油集团有限公司(CNOOC)和法国道达尔能源公司(TotalEnergies)透过上海石油天然气交易所(SHPGX)完成了首笔以人民币结算的液化天然气(LNG)贸易,该交易所在声明中表示,这笔交易涉及到从阿拉伯联合大公国(UAE)进口约6万5000吨液化天然气。
该司向路透社证实了这笔交易,但未对此发表进一步评论。中国海洋石油集团有限公司,目前尚未回应媒体询问。近年来,中国大陆强调用人民币结算石油和天然气贸易,以建立其国际货币的地位,并削弱美元在世界贸易中的影响力。
紧接著本周三(29),沙特阿拉伯国王沙尔曼(Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud)批准了一份合作备忘录,授予沙阿成为上海合作组织(SCO)对话伙伴地位。
上海合作组织成立于2001年,是一个政治、安全和贸易联盟,旨在对抗西方影响力。该组织目前有8个正式成员国,包括中国、俄罗斯、印度、巴基斯坦和4个中亚国家。而伊朗预计将在今年成为联盟的正式成员,去年9月签署了承诺书。
其他中东国家,如卡达和埃及,与沙特阿拉伯一样,与华盛顿有密切的军事联系,同时也是上海合作组织的对话伙伴,这是成为正式成员的第一步。
同日,巴西和中国大陆达成协议,放弃美元,采用各自的货币进行贸易,这将使得中国大陆和巴西能够直接进行贸易和金融交易,互换人民币和雷亚尔(BRL),而不用先将货币转换为美元来进行结算 。
巴西贸易和投资促进局(ApexBrasil)表示,这种新安排预计能够“降低成本”、“促进更大的双边贸易,并促进投资”。
根据最新数据,中国大陆是巴西最大的贸易伙伴,占所有进口商品的5分之1以上,其次是美国。中国大陆也是巴西最大的出口市场,占所有出口商品的3分之1以上。
也是本周三(29),东南亚国协10国(ASEAN)财政部长和央银行总裁的官方在印尼召开会议,首要议程是讨论如何减少对美元、欧元、日元和英镑等主要货币的依赖,转而使用本地货币来进行贸易结算。
会议讨论了通过本地货币交易(LCT)计划减少对主要货币的依赖的努力。这是前一个本地货币结算(LCS)计划的延伸,该计划已经开始在东协成员国之间实施。
这意味著东协跨境数位支付系统将进一步扩展,允许东协国家使用本地货币进行贸易。印尼、马来西亚、新加坡、菲律宾和泰国已于2022年11月达成有关此类合作的协议。此前,印尼的银行监管机构表示,印尼央行正在准备推出自己的国内支付系统。
印尼总统佐科威(Joko Widodo)敦促地区政府开始使用当地银行所发行的信用卡,并逐渐停止使用外国支付系统例如VISA, Mastercard等。他认为,印尼需要保护自己免受地缘政治干扰,他援引了美国、欧盟及其盟友因为乌俄战争,对俄罗斯实施的金融业制裁。
佐科威还强调,摆脱西方支付系统对保护交易免受“可能的地缘政治后果”至关重要。
The IMF warns of the US dollar losing dominance after sanctions
31 MAR 2022
The IMF's top official has warned of a decrease in the US currency's dominance in global markets after imposing sanctions on Russia.
Gita Gopinath, first deputy managing director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), has warned of a gradual decrease of the dominance of the US dollar in the world financial systems after the unprecedented financial sanctions imposed on Russia after its incursion in Ukraine.
The sanctions, from restrictions on Russian banks to measures targeting its economy, imposed by Western nations, could cause a more fragmented international monetary system.
“The dollar would remain the major global currency even in that landscape, but fragmentation at a smaller level is certainly quite possible,” Gopinath told the Financial Times.
“We are already seeing that, with some countries renegotiating the currency in which they get paid for trade,” she added.
Ahead of sweeping Western sanctions, Russian President Vladimir Putin said on Thursday that he had signed a decree saying foreign buyers must pay in roubles for Russian gas from April 1.
The contracts would be halted if these payments were not made.
"In order to purchase Russian natural gas, they must open rouble accounts in Russian banks. It is from these accounts that payments will be made for gas delivered, starting from tomorrow," Putin said.
"If such payments are not made, we will consider this a default on the part of buyers, with all the ensuing consequences. Nobody sells us anything for free, and we are not going to do charity either — that is, existing contracts will be stopped."
The decision is the last step of Russia's long campaign to reduce its dependence on the dollar.
Although the US currency has an outsized role in global markets, its dominance has been gradually decreasing in the last two decades.
According to a recent IMF report on dollar dominance in global markets, “the share of reserves held in US dollars by central banks has dropped by 12 percentage points since the turn of the century, from 71 percent in 1999 to 59 percent in 2021.”
The decline of US dollar dominance is not the result of reserve accumulation by a small number of large reserve holders with a preference for non-dollar currencies.
Rather, the IMF sees the active portfolio diversification by central bank reserve managers as the main reason for this decline.
The share of nontraditional reserve currencies, defined as currencies other than the US dollar, euro, Japanese yen and British pound sterling, rose from negligible levels at the turn of the century to roughly $1.2 trillion and 10 percent of total identified reserves in 2021.